![]()
Part 1 Principles
1. Fluorescence microscope
2. Filterset
in FL-Mic
3. How concocal differs?
4.
What is confocal?
5.
Resolution in confocal
6. Optical
sectioning
7. Confocal image formation
and
time resolution
8. SNR in
confocal
9.
Variations of confocal
microscope
10. Special features from
Leica sp2 confocal
Part 2
Application
1. Introduction
2.
Tomographic view
(Microscopical CT)
3. Three-D reconstruction
4. Thick specimen
5. Physiological study
6.
Fluorescence detecting
General
consideration
Multi-channel detecting
Background correction
Cross-talk correction
Cross excitation
Cross emission
Unwanted FRET
Part
3 Operation and
Optimization
1.
Getting started
2. Settings in detail
Laser line
selection
Laser intensity and
AOTF control
Beam
splitter
PMT gain and offset
Scan
speed
Scan format, Zoom
and Resolution
Frame average, and
Frame accumulation
Pinhole and Z-resolution
Emission collecting rang
and Sequential scan
When Do
you need confocal?
FAQ
Are
you abusing
confocal?
Confocal Microscopy tutorial
Part 1 Principles of Confocal microscopy
3. the differences between conventional and confocal microscope
Extended light versus point light source illumination
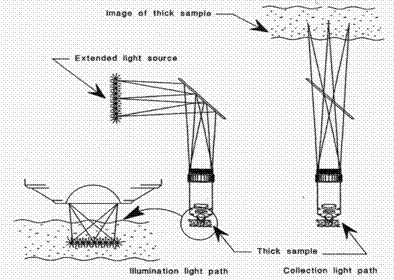 In
conventional wide field microscope, ordinary extended light is used as light
source, the specimen is lit laterally and vertically at the same time as shown
in the illustration. The resulting image is affected by all the lit spots
from the whole illuminated field, although it is centered at a
given focal plane and local spot. These illuminated dots interfere with each
other laterally and the stray light compromise image contrast. Image contrast,
defined as the difference between the minimum and maximum intensity of two
points in the image, is an important factor for an optical device to achieve its
resolution, without proper contrast, the signal has little difference with
background and the resolution of the an optical lens can
not be realized. Improved contrast helps an optical device to reach its
maximum resolution.
In
conventional wide field microscope, ordinary extended light is used as light
source, the specimen is lit laterally and vertically at the same time as shown
in the illustration. The resulting image is affected by all the lit spots
from the whole illuminated field, although it is centered at a
given focal plane and local spot. These illuminated dots interfere with each
other laterally and the stray light compromise image contrast. Image contrast,
defined as the difference between the minimum and maximum intensity of two
points in the image, is an important factor for an optical device to achieve its
resolution, without proper contrast, the signal has little difference with
background and the resolution of the an optical lens can
not be realized. Improved contrast helps an optical device to reach its
maximum resolution.
Whole length image versus optical section
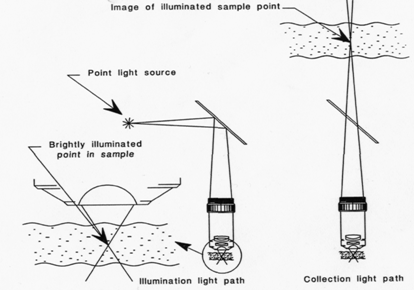 If
a point light source illumination is used, only one point in the specimen is lit
at a time and the resulting image therefore is void of those lateral interference
of dots in extended light illumination.
But here the lit spots from above and under-focal plane still exists since light
pass through it. The images from out-focal-planes overlaps on the
focal plane, thus the image sharpness is compromised. To be worse, weak signals
from a given plane of the specimen can be totally un-detectable because they are
buried within the mixture. This is more dramatic in thick specimen where a
sharp focus can not be achieved at all.
If
a point light source illumination is used, only one point in the specimen is lit
at a time and the resulting image therefore is void of those lateral interference
of dots in extended light illumination.
But here the lit spots from above and under-focal plane still exists since light
pass through it. The images from out-focal-planes overlaps on the
focal plane, thus the image sharpness is compromised. To be worse, weak signals
from a given plane of the specimen can be totally un-detectable because they are
buried within the mixture. This is more dramatic in thick specimen where a
sharp focus can not be achieved at all.
In another configuration, a plate
with a small hole called pinhole is placed before the image detecting device like below:
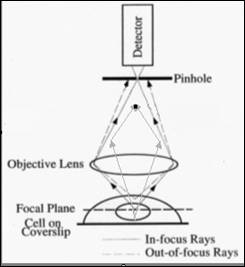 In this configuration,
light from under-focal-plane will be focused at a plane behind the pinhole such
is blocked away by the pinhole plate. The light from above-focal-plane will be
focused before the pinhole and is blocked away by the pinhole too. Only
the light from focal plane is just focused at the pinhole thus can reach the
image detector. This process simulates what you do with a microtome to cut some
unwanted tissue away, but you do it here optically, this is so called "optical
sectioning".
In this configuration,
light from under-focal-plane will be focused at a plane behind the pinhole such
is blocked away by the pinhole plate. The light from above-focal-plane will be
focused before the pinhole and is blocked away by the pinhole too. Only
the light from focal plane is just focused at the pinhole thus can reach the
image detector. This process simulates what you do with a microtome to cut some
unwanted tissue away, but you do it here optically, this is so called "optical
sectioning".
The size of pinhole determines how thick an optical slice will be. The smaller the pinhole, the thinner the slice. But the thickness will not go down indefinitely. It is also limited by all those factors affecting resolution of the lens: the wave length of light, Numerical aperture of the lens, reflecting index of media, together with pinhole size, the z-resolution is usually 2 times worse than lateral resolution of an objective. For a lens of 1.4 NA, blue light at 488 nm, the lateral resolution is 200 nm, the achievable optical section thickness is about 400 nm.
Statement about this web and
tutorial
For problems or questions regarding this web contact
e-mail:
This page was last updated
23.03.2004